With this new part we will now be covering the BYOD device management strategies this time we will be focusing primarily on how we will manage the overall device enrolment.
Separation Between Corporate Devices vs BYOD device
Before we actually go into various areas of Endpoint Manager, we first need to define our criteria for our corporate devices and our BYOD Devices.
Corporate Device Definition
We may overlap with the definitions as these may already be familiar to you but will help further on this part as well as through the entire series.
Typically, we would categorize these devices as being provided by the organization to the end user. Whilst these devices are onboarded or pre-provisioned, they will then be part of the MDM management which they will receive company standard policies such as:
- Compliance Policies
- Configuration Profiles
- Security Baselines
- Company Standard Applications
- Conditional Access policies
BYOD Device Definition
These devices are essentially devices in which users bring their own, but in order for these devices are able to be utilized within the organization they must meet certain criteria before they can actually be allowed to access company resources.
Effective BYOD Device Enrolment
Strategies for Seamless Management
These category summarizations will help to set the tone for the overall part where we will go deeper into the enrolment side. The key goal is to ensure we have a separate workflow set aside from the corporate device workflow so we have a different process altogether.
BYOD Process Chain
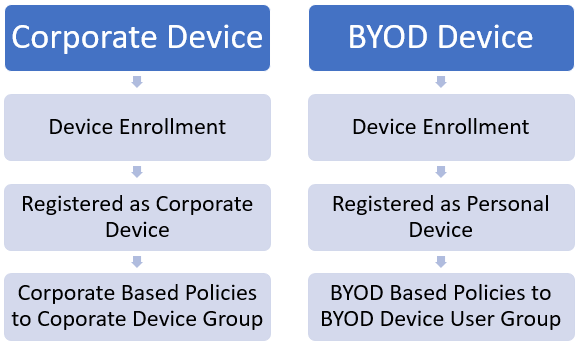
Figure 1.1 – Device Enrollment process diagram
The above diagram gives a visual for the process of both. But here is where we need to do the most planning to understand how we grade a BYOD device as compliant before it joins our management.
Things to take in consideration are things such as:
- Type of device models used.
- Whitelisted Enrolment methods
- Authentication methods
- Regional Areas of access
- Mandatory Applications
- Baseline Levels
These have to all be taken into account, and these carefully planned will make the below sections much easier to make the choices on how we will move forward with setting up our BYOD environment.
BYOD Device Enrolment Methods
Limiting Device Enrolment Methods
Another area to take into consideration in regard to the device enrolment is also the security aspect. Whilst organizations may accommodate personal device enrolment, what we don’t want to do is to have every single device type have this option.
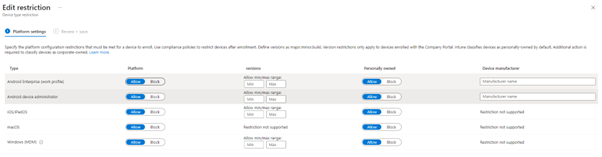
Figure 1.2 – Enrollment Method Restrictions
With this configured we can then limit which methods we would allow for devices to enroll via BYOD users.
Windows
Company Portal
One area we can look at for Windows devices can be from when we very first set up a device whether that device has actually had a new OS installed.
Either Windows 10 or Windows 11 will provide you with an option to sign into your work or access your school account where you can use your company credentials to sign in.
Typically, an ESP page is in conjunction with the Autopilot device process which is more of a corporate-managed process, whereas a straight sign-in on the device will go through just the ESP page by default.
This can technically make the device more corporate base with a manual intervention of changing the device category to personal.
Once this has been done, you would be able to see the Enrolment Status Page which would then process the configuration of the device before it’s able to access the network. Here, having an ESP available for BYOD devices would be a great way to accommodate these devices in cases like this. This scenario may perhaps fit more for virtual machines but can be cases where brand-new devices are bought personally.
Example:
Let’s take for example the default ESP which has the lowest priority set.
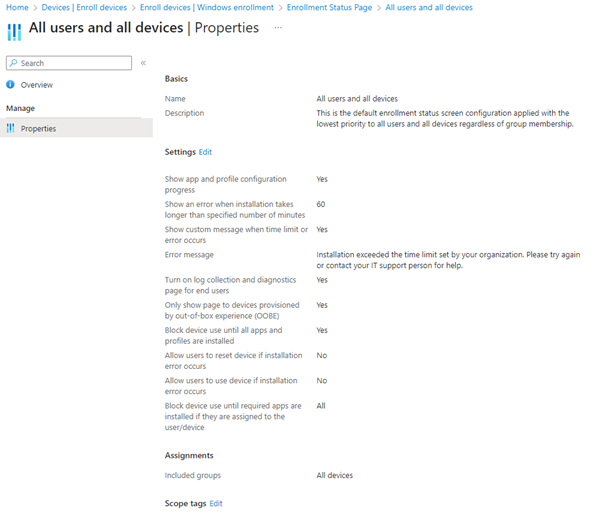
Figure 1.3 – Default Enrolment Status Page
This would be by default every device would see whether going by Autopilot or signing the device into the Work or Access school account. Now if we have an ESP created and dedicated to a group that would contain your BYOD device users, you will then have a set structure ready for the onboarding of those devices into your endpoint manager environment.
Android
Android Enterprise
With non-Windows methods, you may find there are easier methods of creating the separation between the corporate device and personal device enrolment.
For this, it would be the Android Enterprise section where we would define a google play business account.
iOS/MacOS
Apple MDM Certificate
To unlock the creation of the enrolment profiles for iOS devices you need to establish the creation of the Apple MDM certificate which you can obtain from following the process using business apple ID to generate the certificate.
The process is slightly different in regard to how the separation between corporate devices and personal devices is concerned. If you have gone through the apple business device configuration you may be issued enrollment program tokens which can be issued to Apple devices that would be recognized as corporate devices. For personal devices, at least perhaps a better fit for personal devices would be to utilize the Company Portal app on iOS devices. You can of course create enrollment profiles that can configured to be aimed at specific groups. In this case, we would assign this to a group that would contain the users that would be using the BYOD process.
Enrollment Notifications
This area is more aimed at the user experience after a device has been onboarded. Enrollment notifications can be extremely useful to let either the end-user or the internal support team for the organization as an example.
So, If we take a look at Figure 1.3 and Figure 1.4 we see we have a couple of options as to how these notifications can be distributed
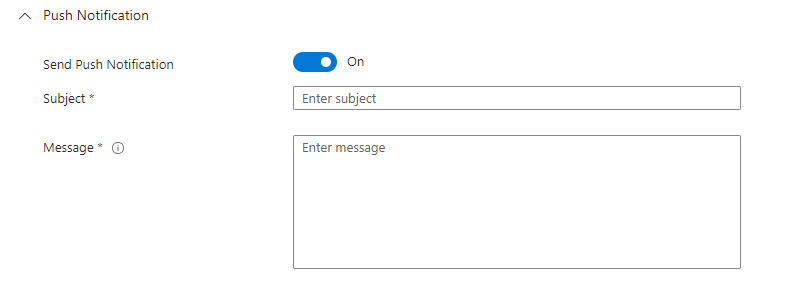
Firstly, we have push notifications which will present the subject and message to the onboarded device. This can contain confirmation details and next steps which can be very key for BYOD device users. The next option is email notifications. We can see an example of the configuration from within.
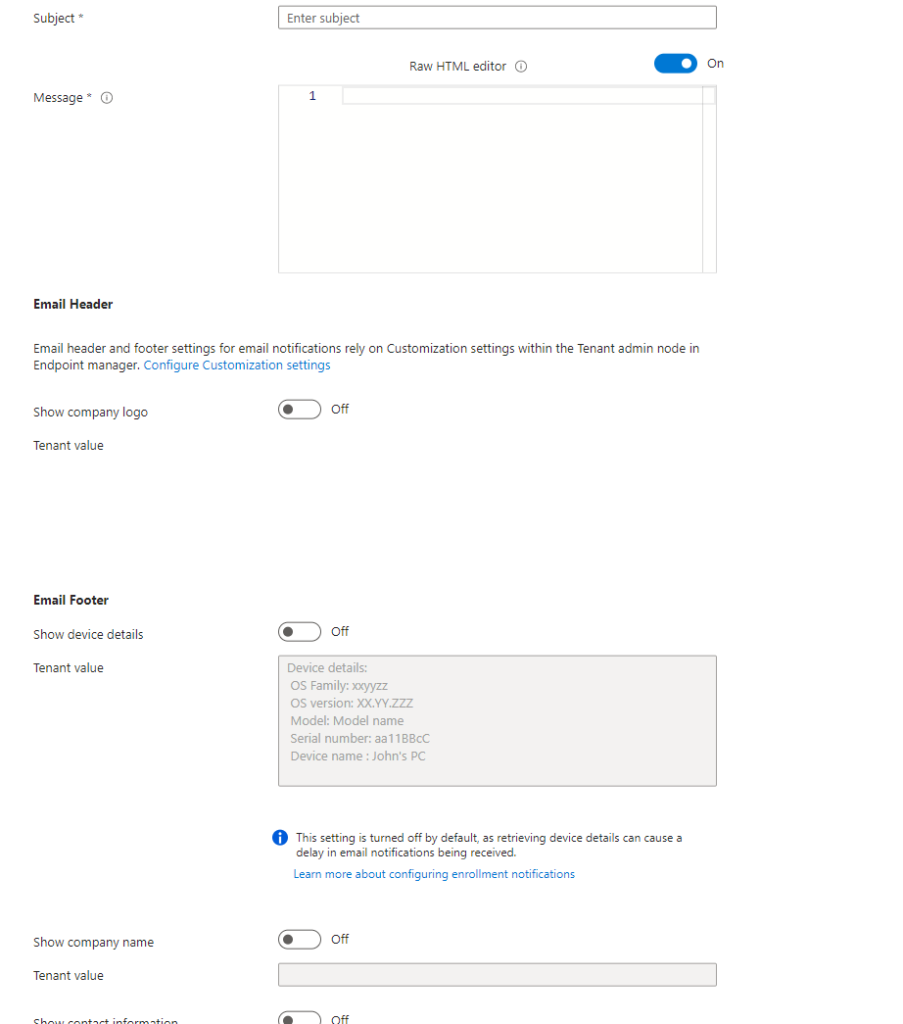
Figure 1.4 – E-mail Notification Details
E-mail notifications which can be tailored a lot more specifically and with this in mind can have various uses where they can be sent to the primary user of the device, the Internal support team for confirmation, and even security teams for audit purposes.
Next On Part 3
In the next part of the series, we will look at the planning of Configuration Profiles and Conditional Access policies for BYOD Devices.
You can read the previous article by clicking here.






